最近克隆一个项目,为了加快速度和节省空间,在克隆的时候设置了 depth=1 也就是只记录最近一次提交,在 SourceTree 里操作如下
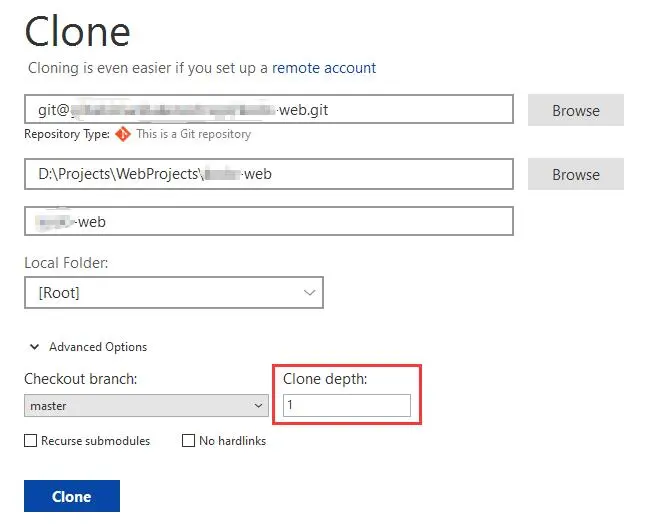
克隆之后文件历史如下,只会有一行记录
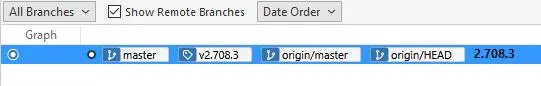
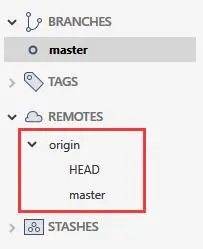
此时想要切换分支发现远端分支显示不全,只有浅克隆的分支。
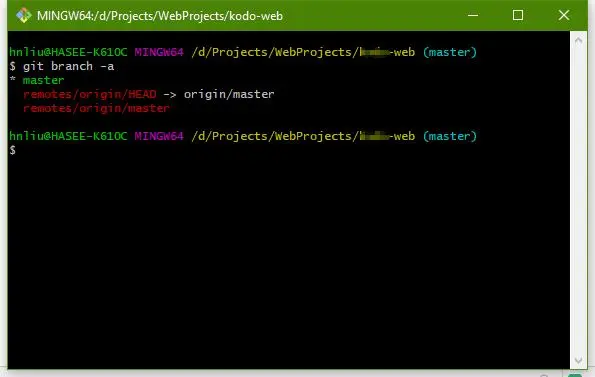
执行 git branch -a 显示也是如此
经过查询文档 git-remote - set-branches
找到了 git remote 命令,用来管理追踪的远程分支,其中 set-branches 命令用来更改追踪的分支,可以在仓库设置完成后来追踪新的远程分支。这里直接使用
git remote set-branches origin '*',如果只想追踪某个分支,也可以使用 git remote set-branches origin 'branch-name'
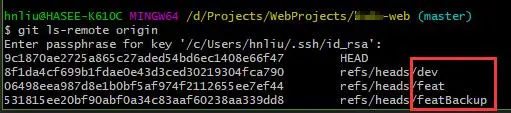
命令。不确定分支名字可以使用 git ls-remote origin 命令查看,origin 后面只需要跟红框中的名字就行。
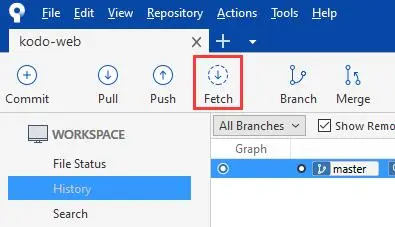
最后要做一次 git fetch -v,在 SourceTree 中就是 Fetch。
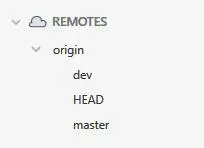
然后就可以看到添加的远程分支了。
最后,根据文档 git-clone - depth
中的说明,造成看不见其他分支的原因,还是因为在 clone 的时候使用了 --depth 参数相当于使用了 --single-branch
参数,此时只需要加上 --no-single-branch 即可。如果希望其他分支也是 shallow clone,则需要使用 --shallow-submodules
命令。粗略翻了一下,没有在 SourceTree 克隆界面发现相关设置,可能还是需要用命令来实现以上需求。